
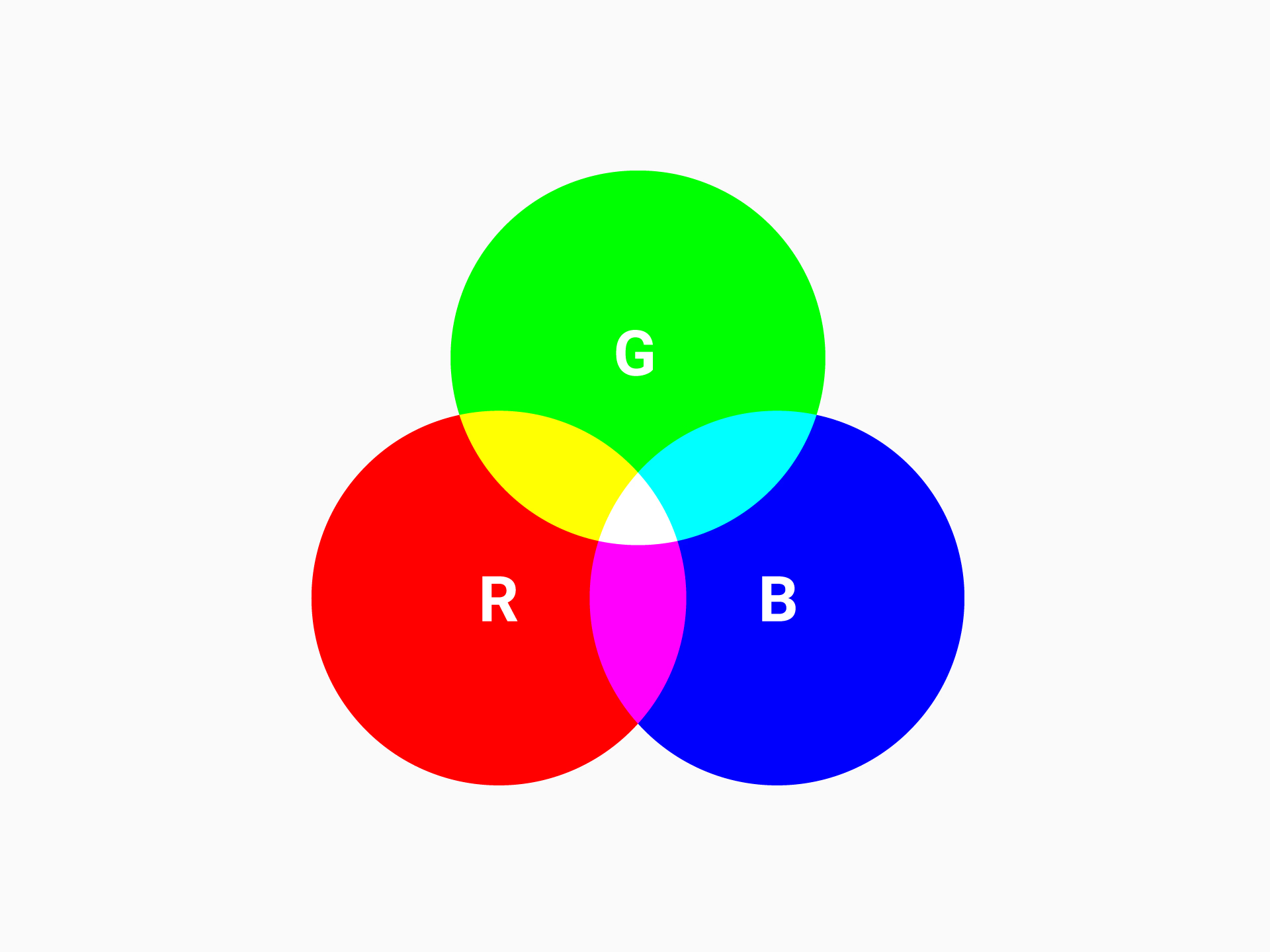
ကာလာ အရောင် မှာ အပြော အများဆုံး က RGB & CMYK ပါ။ သူ့နောက်မှာတော့ Pantone/PMS & RAL ပေါ့။
| System | Model | Primary Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGB | Additive (light) | Digital screens, web, computer monitors, TVs | Combines red, green, and blue light to create colors; used for digital media. |
| CMYK | Subtractive (pigment/ink) | Printing (magazines, brochures), some at-home printers | Uses cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks (key) on a white surface; colors get darker when mixed. |
| RYB | Subtractive (pigment/paint) | Traditional art, painting classes | The historic artist’s color model using red, yellow, and blue as primary colors. |
| Pantone Matching System (PMS/FHI) | Spot Color | Branding, packaging, textiles, product design, paints | A standardized system with specific, pre-mixed colors identified by unique numbers to ensure global consistency across materials. |
| RAL | Spot Color | Coatings, architecture, construction, automotive industry | A popular European standard, primarily for defining standard colors for powder coating, varnish, and plastics; uses a 4-digit code (RAL Classic). |
| NCS | Perceptual | Architecture, interior design, manufacturing | The Natural Color System is based on how humans perceive color (hue, saturation, brightness) and is used globally as a logical standard. |
| Munsell | Perceptual | Color science, specific industrial use (e.g., soil, beer) | Organizes colors into a 3D solid based on hue, value (lightness/darkness), and chroma (saturation/brightness). |
CMYK for Print

RGB for Web & Screen / Digital
Pantone for Color Accuracy

RAL Colors for Coatings

Source
Snowball | Color Systems: CMYK, PANTONE, RGB and RAL explained
